DIAMONDS ARE THE HARDEST NATURAL SUBSTANCE KNOWN TO MAN.
FORMED OVER MILLIONS OF YEARS, EVERY DIAMOND IN THE WORLD IS UNIQUE.
Buying a diamond should be based on the right knowledge, as they come in many qualities.

The four C’s are used worldwide to describe the quality of diamonds. They are:
The interrelationships of these characteristics greatly
affects the value. The rarest and most valuable diamonds are the
clearest and purest of color. Other factors that determine a diamond’s
quality and value are its symmetry and cut proportions. Learning as much
as possible about the differences in quality and value will help you
choose the right diamond.
COLOR
Diamonds come in all colors of the rainbow – some of which are more expensive than the others.
With
the exception of blue, pink and red diamonds (which are in the “fancy
colors” category of diamonds), “colorless” diamonds are the most
valuable. As mentioned before, the diamond’s beauty lies in the fact
that it acts as a prism. But the presence of color seriously limits the
diamond’s ability to act as one, thus, the less color the better.

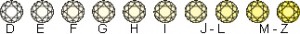
The
Gemological Institute of America created an alphabetical grading scale
for the degree of color in a “colorless” diamond. The scale goes from
“D” (least amount of color) to “Z” (yellow color). Anything over a “Z”
rating falls into the “fancy colors” category.
CLARITY
Again, you want a clear diamond to allow the light to
pass through the diamond with the least amount of obstructions. Besides
color, another obstruction would be interior and exterior inclusions
(also known as carbon spots or flaws), minute traces of mineral trapped
in a diamond during the crystallization process. Clarity refers to the
number, colour, size and position of these inclusions. The purest
diamonds are graded as “Flawless”.

CARAT WEIGHT
Diamonds are measured in terms of weight, not size. One
carat is equal to 100 points. Two diamonds of equal weight can have very
different values, because the quality is still determined by the color,
clarity and cut.

CUT
Cut is the only diamond characteristic directly
influenced by man. The artistry and technical knowledge the master
cutter applies while placing the facets on the diamond greatly affect
the value. If the stone is too deep, light is lost through the sides, if
too shallow light is lost through the bottom facets. So the better a
diamond is cut, the more sparkle it will have.
The shape of a diamond is a personal choice and does not materially effect its value.
Here are seven of the most popular diamond cuts:

Source: D. Blackman
|